An autonomous mobile robot, or AMR, is at the confluence of artificial intelligence and the fusion of data from multiple sensors.
This ingenious convergence paves the way for a variety of applications, but it is most notable in the field of autonomous mobile security robots, redefining safety standards in high-risk environments.
The fundamental distinction between Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) lies in their approach to navigation and automation. AGVs, as their name suggests, rely on pre-established guides such as magnetic strips, lines painted on the ground or specific sensors to follow a predefined route. This approach fixes AGVs in pre-configured environments, limiting their flexibility in dynamic environments.
AMRs, on the other hand, make full use of advances in AI for autonomous navigation. They are equipped with a sophisticated array of sensors, artificial intelligence and machine learning to calculate, interpret and plan their trajectory. For example, the GR100 robot is equipped with cameras and sensors that enable it to navigate avoiding obstacles. It slows down, stops or recalculates its path if it encounters an unexpected obstacle.
Features of an autonomous mobile robot like the GR100:
Technologies such as LiDAR sensors, simultaneous localisation and mapping (SLAM) enable this robot to determine the best route between waypoints.
An autonomous mobile robot dynamically plans the shortest trajectory according to prevailing conditions and requirements. If its patrol changes overnight, the robot's route also changes. At Running Brains Robotics, permanent and temporary no-go zones can be defined for the surveillance robot to avoid.
The AMR robot automatically detects and avoids obstacles and blocked routes to find the best trajectory to the next point of passage.
The robot will automatically recharge when its mission is complete or when its charge is estimated to be too low. This is the case with the GR100 robot, which keeps a static watch even on its charging dock.
This ability to adapt in real time means that mobile robots can navigate autonomously in complex and changing environments, eliminating the need for a dedicated infrastructure. In short, while AGVs operate on fixed, pre-established routes, AMRs chart their own course using advanced AI algorithms, offering unrivalled flexibility in changing environments.
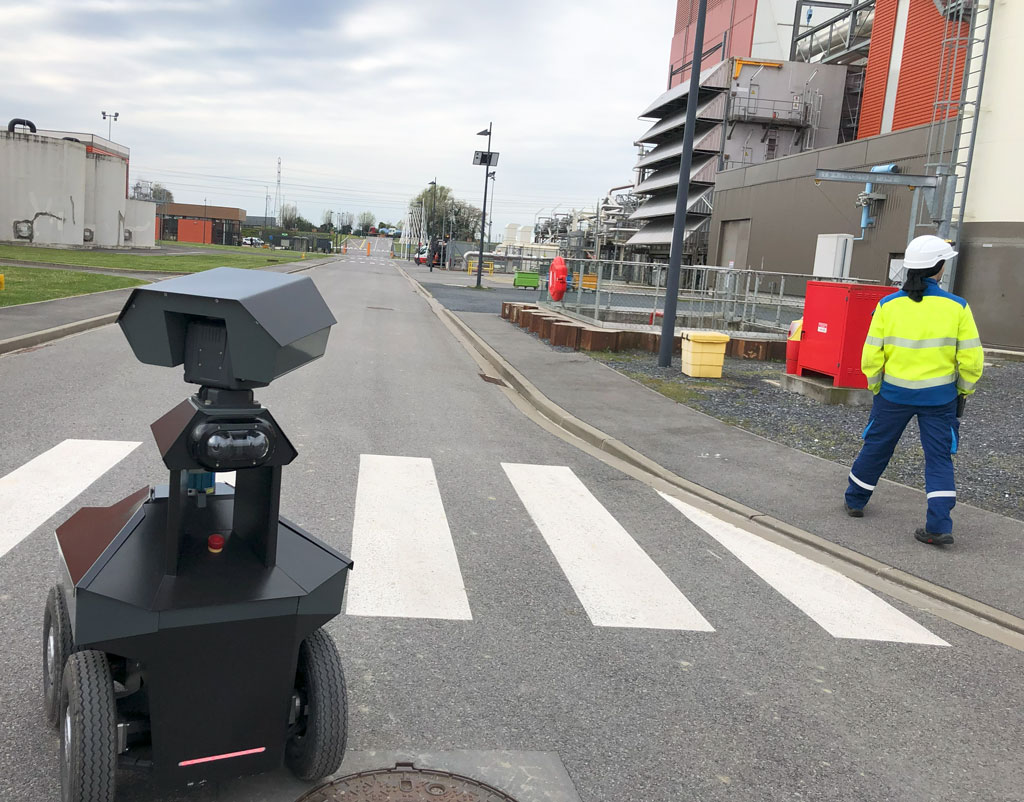
The role of AMRs also extends to the sensitive areas of security and safety. Autonomous mobile security robots, such as the GR100, patrol high-risk sites such as industry, ensuring constant surveillance. Their ability to detect anomalies, combined with instantaneous responsiveness, make them invaluable allies in the preservation of property, installations and people.
Seveso sites, industrial sites, logistics sites, ERP facilities, etc. are all looking to innovate in order to improve the operational efficiency, speed, precision, and safety of their teams. Many are turning to autonomous mobile robots (AMR).
In the field of security, autonomous mobile security robots are emerging, redefining the security landscape for high-risk sites such as industry. These surveillance robots, powered by a fusion of AI and multi-sensor data, demonstrate an unrivalled ability to patrol, monitor and react autonomously. Unlike traditional security systems, these robots can anticipate safety or maintenance hazards thanks to their advanced understanding of the environment, minimising risk.
The most intriguing aspect of these robotic guards is their ability to adapt proactively to emerging threats. Advanced sensors pick up subtle signals, while AI rapidly analyses this data, enabling the robot to alert operators to danger.
As autonomous mobile security robots, AMRs are revolutionising the surveillance of high-risk sites. Their ability to patrol autonomously, detect anomalies and alert in real time makes them invaluable allies in maintaining industrial safety. These electronic guards reduce human risks while enhancing the security of sensitive installations.

At the heart of AMR robots lies the fundamental concept of the human-robot relationship. This symbiotic relationship goes beyond simple automation, creating a cooperation in which human skills and algorithms complement each other. Autonomous mobile robots do not replace, but augment human capabilities, offering increased efficiency in dynamic and risky environments.
In conclusion, autonomous mobile robotics, powered by AI and multi-sensor data fusion, transcends the boundaries of automation. Autonomous mobile robots like the GR100 are emerging as key players in redefining the safety of high-risk sites. Their ability to fuse data using complex algorithms, to operate in a variety of environments and to patrol on their own, is broadening the horizons of operational efficiency and safety and security.
More than just autonomous machines, they are technology partners who are positioning themselves as the key players in a new era in which humans and machines work hand in hand.

Head of Marketing & Communication at Running Brains Robotics